Before and After
Before
This word expresses to us that an action had taken place before the indicated moment.
It works in three different ways:
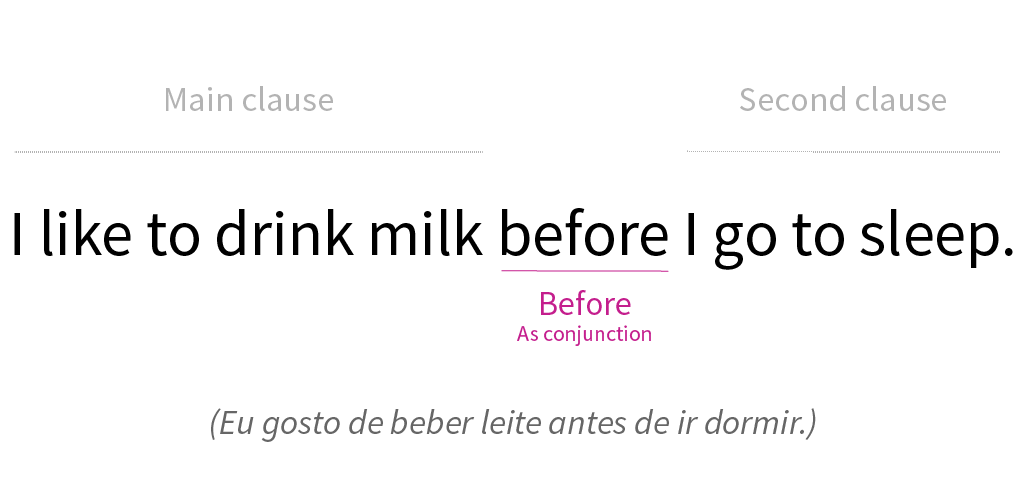
1. As a conjunction:
In this way, "before" joins two clauses. Usually, it precedes the verb in the sentence.
The verbal tense doesn't matter, as long as the sentence doesn't lose its meaning.
2. As a preposition:
In this case, "before" can mean two different things:
- Earlier than:
Alicia came to work before her boss. She was saved by the bell. - In the presence of:
Please stand up before the judge.
3. As an adverb:
In this form, it is used in the following ways:
- In the present perfect tense, when something has happened needs to be made at any time before the current time.
The students have to send their homework before midnight. - In the past perfect tense, when something happened before the current time.
Hadn't we seen that movie before? - If we want to count back from a past moment, using time expressions.
That kind of behavior was not allowed before.
In this case, before is usually found at the end of the sentence. For example:

After
This word expresses to us that the action happens after the indicated moment.
It works in three different ways:
1. As a preposition:
It is followed by a noun. Like this:

2. As a conjunction:
In this case, it connects two clauses.
It doesn't matter if the conjunction opens the sentence or is in the middle of it. The connection is given by the implicit meaning of what you are expressing.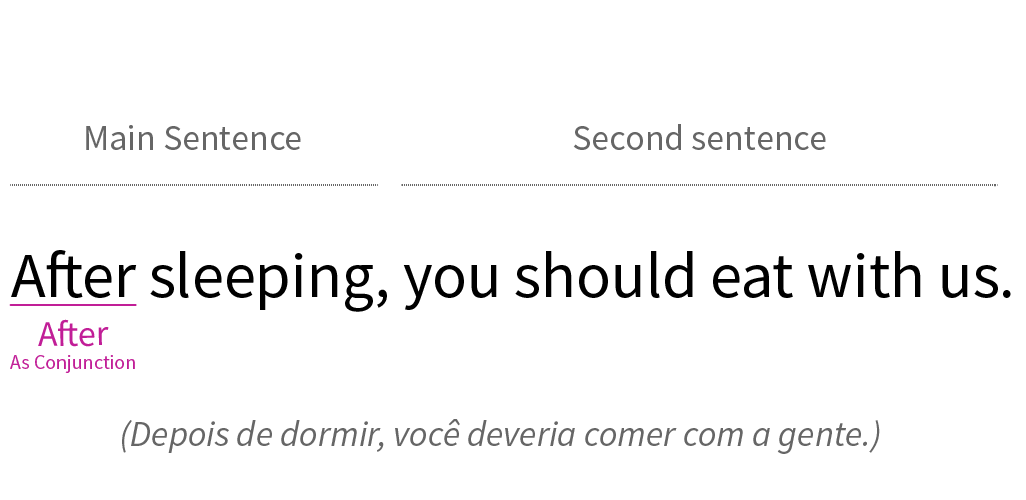
3. As an adverb:
When "after" is used as an adverb, it doesn't precede the noun.
- Dan came to work at 10 o'clock. I came in one hour after him.






